Proteins and micronutrients: Promotes bone and gut health!
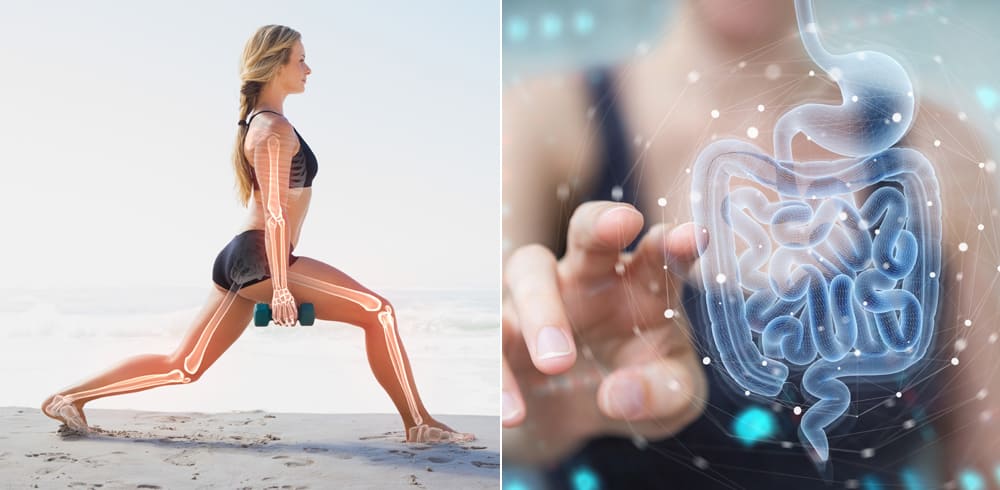

Dietary protein along with micronutrients serve as one of the key representatives in safeguarding bone and gut health.
Healthy bones

Keeping bones healthy is necessary and protecting your bone health is easy but also rather more important than you think. Bone health is important because the process of formation of new bone and break down of old bone occurs continuously throughout your life as soon as you step into your adulthood!1
Healthy diet has a direct influence on bone mass and maintaining a diet rich in proteins and micronutrients can help keep the bones healthy.1,2
Role of proteins in bone health
A diet rich in protein provides amino acids and other essential nutrients responsible for building and maintaining bone tissue. They are also beneficial for the growth of bones and increase calcium absorption.2
Higher muscle mass means higher bone mass and adequate protein ensures an adequate muscle mass which is an important determinant of bone health. Foods rich in protein include dairy foods, meat, poultry, and fish, as well as eggs. Other sources of protein are vegetables like legumes (e.g. lentils, kidney beans), soya products (e.g. tofu), grains, nuts, and seeds.2,3
As per National Osteoporosis Foundation (NOF), a higher intake of protein is beneficial for bone density and reduces the risk of spine fracture regardless of the animal or plant source of protein.4
Optimal protein intake is particularly important for old age people suffering from osteoporosis, and people who are at risk of malnutrition due to acute or chronic illness, or recovering from an injury.4
Role of micronutrients in bone health
Micronutrients, which comprise of vitamins and minerals plays important role in the maintenance and development of bones. These are needed in minute amounts in the body (that is why the word micronutrients). It is very well-known that they micronutrients like Calcium, which is a mineral and Vitamin D, which is a vitamin that we get from sun are important for bone health. Calcium is one of the most important bone minerals, but it needs vitamin D to get absorbed by the body and incorporated into bones.5,6
Other nutrients that build peak bone mass are calcium and vitamin D with vitamin K, protein, phosphorus, magnesium, and zinc.
Vitamin K has also been found to improve bone mineral density, reduction in fractures, and boost the formation of bone. The benefits of healthy nutrient intake on bone health are further enhanced by regular physical exercise and adopting healthy lifestyle.6
Healthy Gut

The human gut is the most populated area of our body with over 100 trillion of good bacteria living in it. The gut microbiome bacterial world has many functions in our bodies from digesting nutrients, regulating how energy is used, and supporting and boosting our immune system.
Role of Proteins in gut health
Proteins help in the normal functioning of the body as well as keep the gut healthy. Protein-rich food upon digestion gets converted to amino acids and peptides which improves the diversity of the gut microbiome. For example, plant proteins like rice, soy, and wheat can improve the composition of gut microbiota by promoting microbial diversity in the gut microbiome. Soy proteins are considered rich sources of essential amino acids that support the growth and diversity of some gut microbiota by acting as a source of both nutrient and energy sources for good microbes residing in the gut.
Dairy and lean meat protein, when included in the diet at recommended levels proves to be beneficial for the growth and abundance of the bacterial species called Lactobacillus and helps in maintaining a more balanced composition of gut microbiota good bacteria of the gut.
Role of Micronutrients in gut health
A healthy gut is capable of maintaining an optimal immune system and consequently reduces the occurrence of many diseases. Dietary micronutrients such as vitamins and minerals enrich the good gut bacteria and help them to flourish. Dietary vitamins act as a source of energy for gut bacteria. Vitamin A found in meat, fish, and various fruits and vegetables help the gut bacteria to bloom and diversify. Vitamin C, E, and B2 promote antioxidant activity against bad microbes and maintain oxidative balance in the small intestine while Vitamins C and D keep the good bacteria in the gut healthy so that they can effectively break down dietary compounds that together benefit the good bacteria and the person. Several bacteria of the gut microbiome release substances responsible for improving mineral status by the increasing the absorption of calcium, magnesium, iron, and phosphorous.
The final word
Both proteins and micronutrients play an indispensable role when it comes to maintaining and improving both bone health and immunity. Low levels of proteins and micronutrients could have adverse consequences and this issue can be solved by taking appropriate supplements under a doctor’s advice.
References
1. Healthy lifestyle. Available at https://www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/adult-health/in-depth/bone-health/art-20045060 Accessed on 28.12.2022
2. Proceedings of the Nutrition Society (2021), 80, 165–172
3. Protein and other nutrients. Available at https://www.osteoporosis.foundation/patients/prevention/protein-other-nutrients Accessed on 28.12.2022
4. Protein role in bone health. Available at https://nutrition.org/meetings/continuing-education/protein-bone-health/ accessed on 28.12.2022
5. Bonjour JP. Protein intake and bone health. Int J Vitam Nutr Res. 2011 Mar;81(2-3):134-42.
6. https://www.nutri-facts.org/en_US/news/articles/micronutrients-for-bone-health.html

 Buy Now
Buy Now Buy Now
Buy Now



