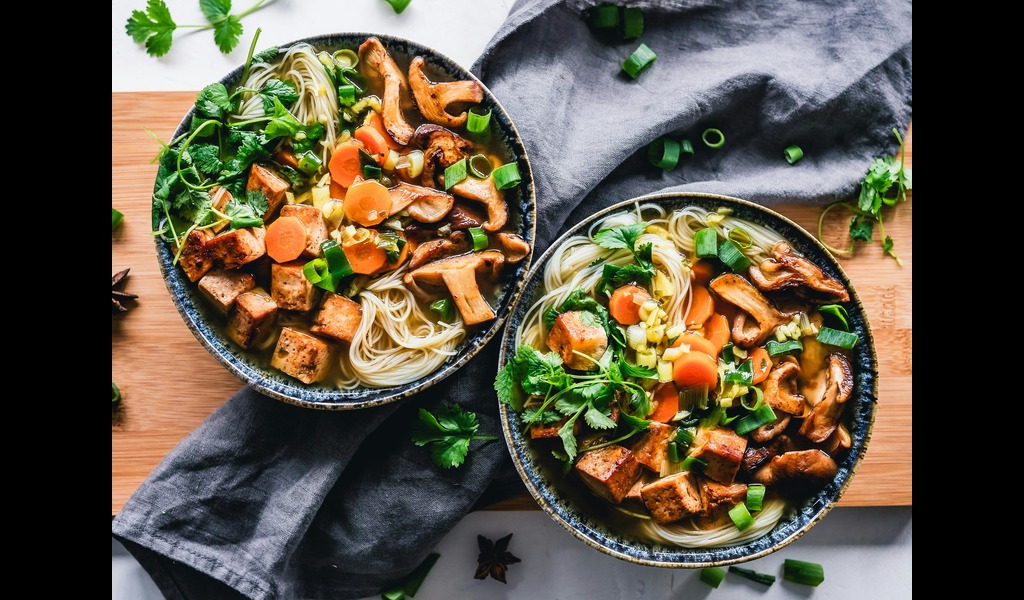
Understanding Protein and Protein-Rich Foods for Vegans

What is Protein?
Proteins, essential for our body’s functioning, are composed of amino acids. Of the twenty amino acids found in nature, nine are essential, meaning our bodies can’t produce them and require them through diet. Animal proteins typically contain all eleven amino acids, whereas plant proteins may have lower amounts.
-
Lentils:
- Protein Content: 8.84 grams per ½ cup serving
- Benefits: Rich in fiber, iron, potassium, folate, manganese, antioxidants
- Source: Nutritional Composition of Lentils
-
Beans:
- Protein Content: Approximately 15 grams per cooked cup
- Benefits: High in carbohydrates, fiber, iron, folate, phosphorus, potassium
- Source: Nutritional Value of Beans
-
Tofu and Tempeh:
- Tofu Protein Content: 10 grams per ½ cup
- Tempeh Protein Content: 15 grams per ½ cup
- Benefits: Soy-based proteins, versatile in cooking
- Source: Soy Protein Content and Health Benefits
-
Green Peas:
- Protein Content: Nearly 15 grams per cooked cup (160 grams)
- Benefits: High in iron, magnesium, vitamins A, C, K, thiamine, folate, zinc, copper, and B vitamins
- Source: Nutritional Value of Green Peas
-
Peanuts:
- Protein Content: Varies (e.g., peanut butter contains 3.6 grams per tablespoon)
- Benefits: High in protein, healthy fats, heart-health benefits
- Source: Peanut Nutrition Profile
-
Almonds:
- Protein Content: 16.5 grams per ½ cup
- Benefits: Rich in vitamin E, healthy fats
- Source: Almond Nutritional Value
-
Chia Seeds:
- Protein Content: 2 grams per tablespoon
- Benefits: High in proteins, iron, calcium, omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants
- Source: Nutritional Composition of Chia Seeds
-
Potatoes:
- Protein Content: 8 grams per large potato
- Benefits: High in carbohydrates, potassium, vitamin C
- Source: Potato Nutrition Facts
-
Protein-Rich Vegetables and Fruits:
- Vegetables like broccoli, spinach, asparagus, sweet potatoes, and sprouts typically contain 4-5 grams of protein per serving.
- Fruits like guava, mulberry, blackberry, and bananas have about 2-4 grams of protein per cup.
-
Nuts and Seeds:
- Benefits: Rich in proteins, fibers, calcium, iron, selenium, phosphorus, vitamin E
- Source: Nuts and Seeds Nutrition Overview
Incorporating these protein-rich foods into a vegan diet can provide essential nutrients and support overall health and wellness.

 Buy Now
Buy Now Buy Now
Buy Now



